Screening Applications & Diagnostics
Poster Session B
(1085-B) Exosome RNA therapy - rapid screening of exosomal RNA cargo for therapeutic applications.
Wednesday, May 29, 2024
10:30 - 11:15 CEST
Location: Exhibit Hall

Christopher DJamoos (he/him/his)
Sr. Strategic Collaborations Manager
Promega Corporation
Brighton, MI, United States
Poster Presenter(s)
Abstract: Exosome RNA therapy - rapid screening of exosomal RNA cargo for therapeutic applications
Authors: Chris D'Jamoos1, et at., Ramin Khanabdali2, Gregory Rice 2,3
1 Promega et al.,
2 Inoviq Limited, Notting Hill, Victoria, Australia.
3 Centre for Clinical Research, The University of Queensland, Herston, Queensland Australia
Abstract
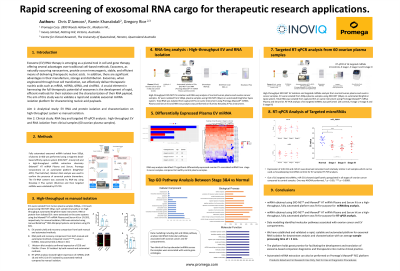
Exosome RNA therapy offers several advantages over cell-based approaches. Exosomes are non-immunogenic, physiochemically stable, do not replicate, display innate tropism and can traverse biological barriers. In addition, there are significant advantages in their manufacture, storage and distribution. Exosomes, when engineered through host cell transfection, can effectively deliver therapeutic nucleic acids such as mRNA, miRNA, siRNA, and circRNA. Requisite to realizing the full potential of exosome RNA therapy are methods to rapidly isolate and characterize their RNA payload. The aim of this study was to validate a rapid and scalable exosomal miRNA isolation platform for characterizing nucleic acid payloads.
Aim 1: Analytical study: EV RNA and protein isolation and characterization on high-throughput system vs manual isolation.
Aim 2: Clinical study: RNA-Seq and targeted RT-qPCR analysis: high-throughput EVand RNA isolation from clinical samples (60 ovarian plasma samples).
Methods: Fully automated exosomal miRNA isolated from 500 µl of plasma (n=60) was performed using a magnetic bead-based affinity capture system (EXO-NET®, Inoviq Ltd) and a high-throughput miRNA extraction kit (Maxwell® HT miRNA Plasma and Serum, Promega) on an automated platform (KingFisher APEX, ThermoFisher). Western blot analysis was used to confirm the presence of canonical protein biomarkers. The EV-RNA content was assessed by RNA seq using NovaSeq X Plus system (Illumina) and then targeted miRNAs were validated by RT-PCR.
Results: Exosomal miRNA isolation from 60 plasma samples was performed in less than 2 hours. Western blot analysis confirmed the presence of exosomal protein biomarkers (CD9 and flotillin-1). Small RNA seq analysis identified more than 400 miRNAs in plasma derived exosomes. Further targeted miRNA analysis by RT-PCR showed abundancy and consistent expression of miR191 (Ct: 22.43±1.87), miR-21 (Ct: 21.98±1.96) and miR-186 (Ct: 24.59±2.03) in all plasma samples.
Conclusion: We have established and validated a rapid, scalable and automated platform for exosomal RNA isolation for downstream analysis and characterization. The platform holds great promise for facilitating the development and translation of exosome-based companion diagnostics and therapeutics into routine clinical practice.
Authors: Chris D'Jamoos1, et at., Ramin Khanabdali2, Gregory Rice 2,3
1 Promega et al.,
2 Inoviq Limited, Notting Hill, Victoria, Australia.
3 Centre for Clinical Research, The University of Queensland, Herston, Queensland Australia
Abstract
Exosome RNA therapy offers several advantages over cell-based approaches. Exosomes are non-immunogenic, physiochemically stable, do not replicate, display innate tropism and can traverse biological barriers. In addition, there are significant advantages in their manufacture, storage and distribution. Exosomes, when engineered through host cell transfection, can effectively deliver therapeutic nucleic acids such as mRNA, miRNA, siRNA, and circRNA. Requisite to realizing the full potential of exosome RNA therapy are methods to rapidly isolate and characterize their RNA payload. The aim of this study was to validate a rapid and scalable exosomal miRNA isolation platform for characterizing nucleic acid payloads.
Aim 1: Analytical study: EV RNA and protein isolation and characterization on high-throughput system vs manual isolation.
Aim 2: Clinical study: RNA-Seq and targeted RT-qPCR analysis: high-throughput EVand RNA isolation from clinical samples (60 ovarian plasma samples).
Methods: Fully automated exosomal miRNA isolated from 500 µl of plasma (n=60) was performed using a magnetic bead-based affinity capture system (EXO-NET®, Inoviq Ltd) and a high-throughput miRNA extraction kit (Maxwell® HT miRNA Plasma and Serum, Promega) on an automated platform (KingFisher APEX, ThermoFisher). Western blot analysis was used to confirm the presence of canonical protein biomarkers. The EV-RNA content was assessed by RNA seq using NovaSeq X Plus system (Illumina) and then targeted miRNAs were validated by RT-PCR.
Results: Exosomal miRNA isolation from 60 plasma samples was performed in less than 2 hours. Western blot analysis confirmed the presence of exosomal protein biomarkers (CD9 and flotillin-1). Small RNA seq analysis identified more than 400 miRNAs in plasma derived exosomes. Further targeted miRNA analysis by RT-PCR showed abundancy and consistent expression of miR191 (Ct: 22.43±1.87), miR-21 (Ct: 21.98±1.96) and miR-186 (Ct: 24.59±2.03) in all plasma samples.
Conclusion: We have established and validated a rapid, scalable and automated platform for exosomal RNA isolation for downstream analysis and characterization. The platform holds great promise for facilitating the development and translation of exosome-based companion diagnostics and therapeutics into routine clinical practice.
